What is Baseball Babip?
Contents
- What is Baseball Babip?
- The History of Baseball Babip
- How is Baseball Babip Used Today?
- The Benefits of Baseball Babip
- The Drawbacks of Baseball Babip
- How to Calculate Baseball Babip
- What Factors Affect Baseball Babip?
- How to Use Baseball Babip in Fantasy Baseball
- How to Use Baseball Babip in Betting
- Conclusion
Babip, or batting average on balls in play, is a baseball statistic that measures how often a batter gets on base.
What is Baseball Babip?
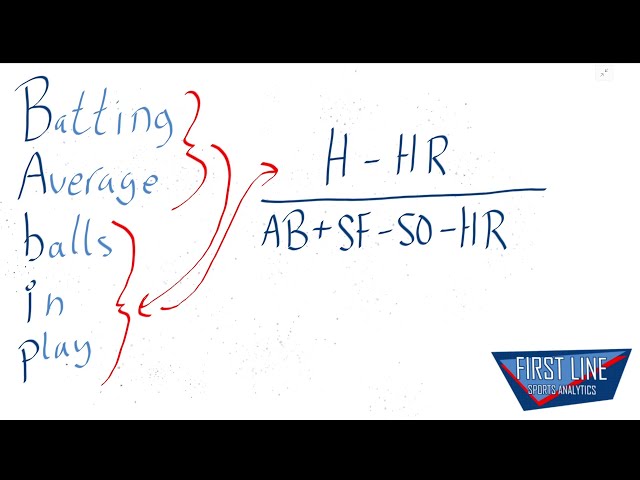
BABIP is a statistic in baseball that stands for batting average on Balls In Play. It is used to measure how often a batter gets a hit when they put the ball in play. The BABIP formula is simple: Hits minus home runs divided by At Bats minus home runs plus Sacrifices.
The History of Baseball Babip
Baseball Babip, otherwise known as batting average on balls in play, is a measure of how often a batter gets a hit when they put the ball in play.
The stat was created by Voros McCracken in an attempt to measure a hitter’s ability to sustain a high batting average and it has become an important tool for evaluating hitters ever since.
Babip is calculated by taking the number of hits that a batter gets divided by their number of plate appearances, minus their home runs
So, if a hitter has 50 hits and 10 Home Runs in 100 plate appearances, their Babip would be .400.
Historically, the league-average Babip has hovered around .300, which means that hitters who are able to sustain a high Babip are typically able to hit for a high batting average
There are a number of factors that can contribute to a high or low Babip, but the two most important are luck and sequencing.
Luck plays a big role in baseball, and it’s impossible to measure how much of an impact it has on individual stats like Babip. However, we do know that over time, luck evens out and players tend to regress towards the mean.
This is why it’s important not to put too much stock into any one year’s worth of data when evaluating players. over the long run, luck will even out and we will get a better sense of each player’s true talent level.
It’s also important to keep in mind that batted balls can be sequences just as easily as hits can be. A hitter who hits a lot of line drives is more likely to have a higher Babip than one who hits mostly fly balls all else being equal.
How is Baseball Babip Used Today?
Baseball BABIP, or batting average on Balls In Play, is a stat that measures how often a batter gets a hit when they put the ball in play. The higher the BABIP, the more lucky a hitter is considered to be. A BABIP of .300 or above is considered to be good, while anything below .300 is considered to be bad luck.
A hitter’s BABIP can fluctuate year to year, and it’s not unusual for even the best hitters to have a down year in BABIP. However, if a hitter’s BABIP drops significantly from one year to the next, it could be an indication that something is wrong. A sudden drop in BABIP can be caused by a number of things, including an injury or a change in approach at the plate.
In recent years BABIP has become increasingly important in baseball analytics. Many analysts believe that a hitter’s BABIP is mostly due to luck and that it’s not a good indicator of future success. However, others believe that there are ways to increase your BABIP and that it can be an important tool in predicting future performance.
The Benefits of Baseball Babip
In baseball, batting average on balls in play (BABIP) is a measure of how often a batted ball falls for a hit. The formula for BABIP is (H-HR)/(AB-K-HR+SF). BABIP can be used to measure the luckiness or unluckiness of a hitter or pitcher. A hitter with a high BABIP is likely to see his batting average regress downwards in the future, while a pitcher with a low BABIP is likely to see his ERA rise.
The Drawbacks of Baseball Babip
The main drawback of using Babip as a metric is that it does not take into account the quality of the contact. A hit off a weak grounder is weighted the same as a home run This can lead to skewed results, especially for power hitters who tend to have higher Babip numbers.
How to Calculate Baseball Babip
Babip, or Batting Average on balls in play, is a statistic in baseball that measures how often a batter gets a hit when they hit the ball into play. The formula for calculating babip is fairly simple: you take the number of hits that a batter gets divided by the number of times that they hit the ball into play. However, there are a few things to keep in mind when calculating this stat:
-You only want to count hits that are not home runs home runs are considered to be “out of play” and do not count towards babip.
-You also want to exclude strikeouts and walks from the numerator and denominator, as these do not count as balls in play.
So, if a batter has 50 hits and 150 plate appearances, their babip would be .333.
What Factors Affect Baseball Babip?
In baseball, batting average on balls in play (BABIP) is a measure of how many hits a batter gets per at-bat. The higher the number, the more hits the batter gets. The average BABIP for all Major League hitters is about .300.
There are a number of factors that can affect BABIP, including the type of hit (e.g., line drive fly ball), the speed of the hitter, and the defense of the opposing team In general, faster hitters and hitters who hit more line drives tend to have higher BABIPs, while slower hitters and hitters who hit more fly balls tend to have lower BABIPs.
How to Use Baseball Babip in Fantasy Baseball
What is Babip in baseball? Babip, or batting average on balls in play, is a statistic that measures how often a batter gets a hit when they put the ball in play. It’s used to measure both a hitter’s fortune and their skill, as hitters with a high Babip are more likely to sustain their success over time.
How is Babip calculated? To calculate Babip, you take the total number of hits that a batter gets when they put the ball in play, and divide it by the total number of times they put the ball in play.
For example, if a hitter has 10 hits and 20 at-bats, their Babip would be .500. If they had 10 hits and 25 at-bats, their Babip would be .400.
What is a good Babip? The league average Babip fluctuates from year to year, but it’s typically between .300 and .310. Hitters with a Babip above .300 are usually considered to be lucky, while hitters with a Babip below .300 are usually considered to be unlucky.
Babip can be used in conjunction with other stats to get a better idea of a hitter’s true talent level. For example, if a hitter has a low batting average but a high Babip, they may be due for some positive regression (meaning their Batting average is likely to go up). Similarly, if a hitter has a high batting average but a low Babip, they may be due for some negative regression (meaning their batting average is likely to go down).
Babip can also be used to identify hitters who are sustaining an unsustainable level of success. For example, if a hitter has an abnormally high BABIP coupled with an abnormally low strikeout rate, there’s a good chance that their performance is due for some major regression.
In summary, baseball babip is A) A stat that measures how often batters get hits when they put the ball in play and B) Used to identify lucky or unlucky hitters as well as those who are sustaining unsustainable levels of success.
How to Use Baseball Babip in Betting
Babip, or batting average on balls in play, is a statistic that baseball bettors can use to find value when wagering on moneylines. Simply put, it’s a measure of how often a hitter gets a hit when they put the ball in play. The higher the number, the luckier the hitter is considered to be. And while there is some luck involved in Babip, it’s also a good measure of a hitter’s true ability.
Conclusion
When a hitter hits the ball hard, there is a good chance it will become a hit. But if the ball is hit softly, it is more likely to be an out. This is where BABIP comes in. BABIP is short for batting average on balls in play. It is a statistic that measures how often a hitter gets a hit when he puts the ball in play.
The league average BABIP is usually around .300. This means that if a hitter puts the ball in play, he has a 30% chance of getting a hit. However, some hitters are able to sustain a BABIP above .300, while others have a BABIP below .300.
A hitter with a sustainable BABIP above .300 is said to have Good luck while a hitter with a sustainable BABIP below .300 is said to have bad luck. However, it is important to note that not all hitters with high BABIPs are lucky, and not all hitters with low BABIPs are unlucky. There are several factors that can affect BABIP, such as speed, defense and hitting skill.