How Do I Calculate Ops In Baseball?
Contents
How do I calculate ops in baseball? It’s a question that every fan asks at some point. Here’s a quick and easy guide to understanding ops and how to calculate it.
What is OPS?
OPS is a baseball metric that combines a player’s on-base percentage and slugging percentage. It is a useful metric for comparing hitters because it takes into account a player’s ability to get on base as well as their power.
What is on-base percentage?
On-base percentage (OPS) is a statistic in baseball that combines a player’s on-base percentage and slugging percentage. The resulting number gives an accurate idea of a hitter’s overall ability as a batter.
OPS = on-base percentage + slugging percentage
For example, if a batter has an on-base percentage of .300 and a slugging percentage of .400, their OPS would be .700. The higher the OPS, the better the hitter is considered to be.
There is no one perfect way to measure a player’s ability, but OPS is a useful tool for comparing hitters. It is important to remember that OPS does not take into account factors such as defense or base running ability.
What is slugging percentage?
In baseball, OPS is a metric that stands for “on-base plus slugging percentage.” OPS is used to measure a player’s ability to get on base and hit for power. It is calculated by adding a player’s on-base percentage and their slugging percentage together.
On-base percentage (OBP) measures how often a player gets on base. It is calculated by dividing the number of times a player gets on base (hits + walks + hit by pitch) by their total number of plate appearances.
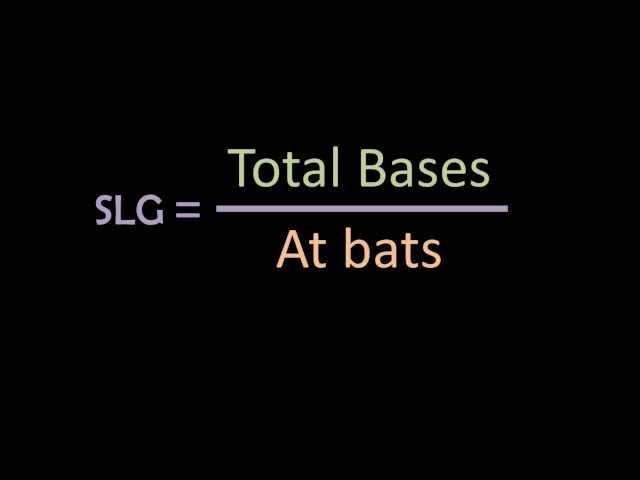
Slugging percentage (SLG) measures how often a player hits for extra bases. It is calculated by dividing the total number of bases a player hits (hits + doubles + triples + home runs) by their total number of at bats.
OPS is considered to be one of the best all-around measures of a hitter’s ability. A high OPS indicates that a hitter is good at both getting on base and hitting for power.
How do I calculate OPS?
OPS or on base plus slugging is a baseball metric that combines a player’s on-base percentage and their slugging percentage.OPS is a good measure of a player’s overall offensive production. A player with a high OPS is typically a good hitter. The average OPS in Major League Baseball is around .700.
On-base percentage
On-base percentage (OPS) is a baseball statistic calculated as the sum of a player’s on-base percentage and their slugging percentage. The name is derived from the fact that it reflects a player’s ability to reach base and hit for power. OPS is one of the standard measures of offensive productivity in baseball. It measures both a player’s batting ability and his power, making it a more complete measure of offensive ability than either on-base percentage or slugging percentage alone.
The on-base percentage portion of OPS is calculated by dividing a player’s total number of times reaching base (hits, walks, and hit by pitches) by his total number of plate appearances. The slugging percentage portion is found by dividing a player’s total number of bases (hits, doubles, triples, home runs) by his total number of at-bats.
OPS values can range from below 0.700 to over 1.500. A high OPS indicates that a player is good at both getting on base and hitting for power, while a low OPS indicates that he is not effective at either one. The most common range for above-average hitters is between 0.800 and 1.000.
Slugging percentage
There are a few different ways to calculate OPS, but the most common method is to simply add a player’s on-base percentage and slugging percentage together. This number can then be used to compare players across all positions and era.
OPS+ is a similar metric, but it adjusts for league and ballpark factors, making it an even better tool for comparing players from different eras.
Why is OPS important?
In baseball, OPS is a statistical measure of a player’s on-base percentage and slugging percentage. The term OPS was first coined by sportswriter John Thorn in the late 1980s. OPS is used to measure a player’s ability to get on base and hit for power. It is important because it is a quick and easy way to compare players across different positions.
OPS as a measure of a player’s ability
OPS is important because it is one of the few statistics that attempts to measure a player’s overall ability. Unlike batting average, which only looks at a player’s ability to hit for average, or home runs, which only looks at a player’s ability to hit for power, OPS looks at both. In addition, OPS gives more weight to a player’s extra-base hits (doubles, triples, and home runs) than singles. This is important because extra-base hits are generally more valuable than singles.
OPS is not perfect, but it is a good way to compare players who play different positions or who have different roles on their team. For example, a corner infielder who hits .280 with 30 home runs and 100 RBI will have a higher OPS than a middle infielder who hits .300 with 10 home runs and 50 RBI. However, the middle infielder may be considered more valuable because he is playing a difficult position and still managing to hit for a high average.
There are other statistics that attempt to measure a player’s overall ability, such as wOBA and WAR. However, OPS is the most common and easiest to calculate.
OPS as a predictor of success
OPS is a baseball statistic that measures a player’s ability to get on base and hit for power. It is often used as a predictor of success, as players with higher OPS totals tend to score more runs and drive in more runs than players with lower OPS totals. The formula for OPS is simple: it is the sum of a player’s on-base percentage and their slugging percentage.
Players with high OPS totals are typically some of the best hitters in baseball. Some of the all-time greats, such as Babe Ruth, Ted Williams, and Barry Bonds, have all posted career OPS totals that are among the highest in history. In recent years, some of the best hitters in baseball, such as Mike Trout, Miguel Cabrera, and Joey Votto, have all posted OPS totals that are among the league leaders.
While OPS is a good predictor of success, it is not perfect. There are some hitters who post high OPS totals but do not score a lot of runs or drive in a lot of runs. These hitters may be good at getting on base but may not have much power or may not play for teams that score a lot of runs. Additionally, there are some players who post low OPS totals but still manage to be successful hitters. These players may not get on base as often or hit for as much power as other hitters, but they may make up for it by being very good at making contact or by playing for teams that score a lot of runs.
How can I use OPS to improve my baseball game?
OPS is a baseball metric that stands for “On-base Plus Slugging”. It is a relatively new stat, but it is gaining popularity because it is a good measure of a player’s all-around offensive ability. OPS can be used to compare players of different positions, to evaluate trade proposals, and to help make decisions about lineup construction.
Use OPS to identify your strengths and weaknesses
OPS is a good stat to use to help identify your strengths and weaknesses as a hitter. If you have a high OPS, that means you’re likely doing a good job of getting on base and hitting for power. If you have a low OPS, that means you may need to work on one or both of those areas.
Use OPS to set goals for your baseball game
OPS is a sabermetric statistic that includes both a player’s on-base percentage and their slugging percentage. OPS is often used to measure a player’s overall offensive contribution.
OPS can be useful for setting goals for your baseball game. If you want to improve your batting average, you can set a goal to achieve an OPS of .750 or higher. If you want to increase your power, you can set a goal to hit 30 home runs with an OPS of 1.000 or higher.






