What Is CTE in NFL Players?
Contents
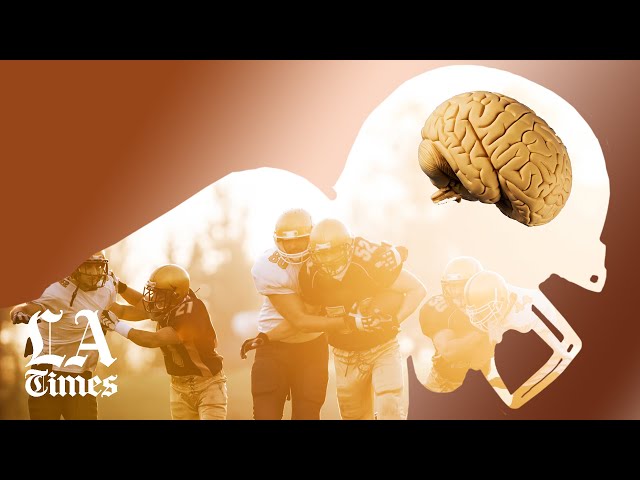
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy, or CTE, is a degenerative brain disease found in people who have had repeated brain trauma. In NFL players, CTE is often found in those who have had multiple concussions.
What is CTE?
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy is a degenerative brain disease found in athletes, military veterans, and others with a history of brain trauma. CTE can only be diagnosed after death and is characterised by brain tissue degeneration and the buildup of a protein called tau. Symptoms of CTE include memory loss, confusion, impaired judgment, impulse control problems, aggression, depression, and, eventually, progressive dementia.
What are the symptoms of CTE?
The symptoms of CTE vary depending on the stage of the disease. People with early stage CTE may experience no symptoms at all. Symptoms of moderate and late stage CTE include:
-Memory loss
-Confusion
-Impaired judgment
-Aggression
-Depression
-Anxiety
-Suicidality
-Parkinsonism
-Dementia
How is CTE diagnosed?
At this time, CTE can only be diagnosed after death. A brain autopsy is needed to confirm the diagnosis. In recent years, however, researchers have developed new ways to identify the protein that is characteristic of CTE, which may eventually lead to a way to diagnose the disease while a person is alive.
How common is CTE in NFL players?
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy, or CTE, is a degenerative brain disease found in athletes with a history of repetitive brain trauma. Symptoms of CTE include memory loss, confusion, impaired judgment, aggression, impulse control problems, depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation. CTE can only be diagnosed posthumously, through an autopsy of the brain.
What are the risk factors for developing CTE?
There are several risk factors that have been identified as contributing to the development of CTE. These include:
-A history of concussions or other head injuries
-A history of playing contact sports
-A family history of CTE
The most significant risk factor for developing CTE is a history of head injuries, particularly concussions. Concussions can occur when the head is hit with enough force to cause the brain to move around inside the skull. This can result in damage to brain cells and the development of symptoms such as confusion, headache, and memory problems.
People who play contact sports such as football, hockey, and boxing are at a higher risk for developing CTE because they are more likely to experience head injuries. Family history is also a risk factor for CTE, which suggests that there may be a genetic predisposition for the condition.
How can CTE be prevented?
There is currently no known cure for CTE, and it can only be diagnosed posthumously. However, there are ways to prevent it. The most obvious way to prevent CTE is to avoid head injuries altogether. While this is difficult to do, especially in contact sports like football, it is important to wear the proper safety equipment and to follow the rules of the game. One study found that tackling with the shoulder, instead of the head, can help reduce the incidence of CTE.Players can also take measures to decrease their risk by building up their neck muscles, which help support the head and limit its movement
What is the NFL doing to address the issue of CTE in players?
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy, also known as CTE, is a degenerative brain disease that has been found in football players who have suffered repeated concussions and head trauma. The NFL has been under fire in recent years for their handling of concussions and CTE, with many retired players suing the league. In this article, we will discuss what the NFL is doing to address the issue of CTE in their players.
What are the NFL’s concussion protocols?
In order to protect its players from the dangers of concussions, the NFL has implemented a number of protocols. These include:
·The NFL Game Day Concussion Protocol, which requires players who show signs of concussion during a game to be removed from the field and examined by a certified trainer or doctor.
·The NFL Pregame Concussion Protocol, which requires players who are suspected of having a concussion to be evaluated by a certified trainer or doctor before being allowed to play in a game.
·The NFL Postgame Concussion Protocol, which requires players who are suspected of having a concussion to be evaluated by a certified trainer or doctor after the game.
·The NFL Return-to-Play Protocol, which requires players who have been diagnosed with a concussion to be cleared by a medical professional before they are allowed to return to practice or play in a game.
What research is the NFL funding?
The NFL has pledged $100 million to support independent medical research into concussion-related injuries, including CTE. The league is also funding research into the treatment and prevention of concussions. Some of the specific areas of focus include:
-Developing better helmets and other protective equipment
-Improving sideline concussion evaluations
-Studying the long-term effects of concussions
-Examining whether certain drugs can help prevent or treat concussions
-Exploring new technologies for detecting concussions
What can be done to help those suffering from CTE?
CTE is a degenerative brain disease that is caused by repeated head trauma. The symptoms of CTE include memory loss, confusion, impulsivity, aggression, and depression. Many NFL players have been diagnosed with CTE after their death. CTE can only be diagnosed after death.
What treatments are available for CTE?
There is no known cure for CTE at this time. However, treatments are available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Common treatments include:
-Medications to help with mood swings, depression, anxiety, and aggression
-Counseling and therapy
-Occupational therapy
-Physical therapy
What is the prognosis for someone with CTE?
There is currently no known cure for CTE, and the best way to prevent it is to avoid head injuries altogether. However, for those who have already sustained brain damage, there are a few treatments that may help to improve symptoms and quality of life. These include:
– Cognitive behavioral therapy: This type of therapy can help to retrain the brain and improve thinking and memory skills.
– Physical therapy: Exercise and physical activity can help to improve brain function and reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
– Medication: antidepressants, antipsychotics, and other medications may be prescribed to help with mood swings, impulsivity, and other behavioral problems associated with CTE.