What Is Pronation In Tennis?
Contents
Pronation is a term used to describe the way your foot rolls when you walk or run. It’s normal for your foot to roll inward when you walk or run. This inward roll is called pronation. When your foot pronates, it provides a natural shock absorption for your body.

Introduction
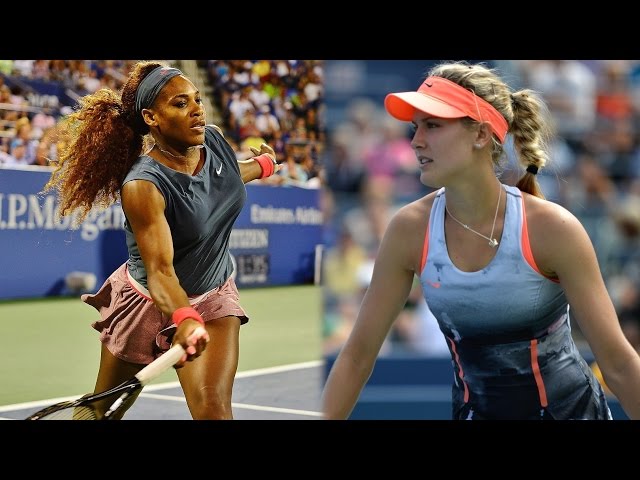
When you pronate, your forearm rotates so that your palm faces the backstop or away from your body. A tennis player who pronates generates power by using a fan-like motion. If you don’t pronate, you may hit the ball flat. Pronation also gives players better control when they hit high balls that bounce near the baseline. When you hit low balls, such as volleys, pronation provides power and accuracy.
What is Pronation?
Pronation is a tennis term that describes the way your foot and ankle roll inward when you walk or run. It’s a natural movement that helps absorb the shock of impact and keep you stable on your feet. But if you pronate too much, it can cause problems.
Excessive pronation can lead to injuries such as Achilles tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, and shin splints. It can also cause your feet to hurt and your shoes to wear out prematurely. If you’re a pronator, you may benefit from using shoes with extra support or stabilizing devices such as arch supports or heel cups.
If you’re not sure whether you pronate, ask your doctor or a certified athletic trainer to watch you walk or run. They can assess your level of pronation and recommend the best treatment options for you.
The Different Types of Pronation
In tennis, pronation is the way your hand and forearm rotate when you make a stroke. There are three different types of pronation: supination, neutral pronation, and extreme pronation. Each type of pronation has its own advantages and disadvantages. Let’s take a look at each one.
Supination
In tennis, there are different types of pronation. Pronation is the term used to describe the way your foot and ankle roll inward when you walk or run. It’s a natural movement that helps with shock absorption and helps keep your balance. When your foot pronates, it allows your lower leg bones to rotate inward. This in turn helps absorb some of the impact from walking or running on hard surfaces.
There are three main types of pronation: supination, neutral pronation, and overpronation. Each type goes through a different type of motion when you walk or run.
Supination (under-pronation) is when your foot rolls outward instead of inward. This can cause problems because it doesn’t absorb shock as well and can put more stress on your joints.
Neutral pronation is when your foot rolls inward at a normal rate. This is considered the ideal type of pronation because it provides good shock absorption and allows for a natural range of motion.
Overpronation (over-pronation) is when your foot rolls inward too much. This can cause problems because it puts extra stress on your joints and muscles, and can lead to injuries such as plantar fasciitis (heel pain) or Achilles tendonitis (ankle pain).
Pronation
Pronation is a type of spin where the ball rotates clockwise when viewed from above. It is the most common type of spin used in tennis and is usually generated by a forehand stroke. The main advantage of pronation is that it provides more topspin than other spins, making the ball dip more quickly and giving it more forward momentum once it bounces. This makes it difficult for opponents to hit the ball cleanly and increases the likelihood of them making errors. Pronation is often used by players who rely on their forehand as their primary weapon, such as Rafael Nadal and Roger Federer.
There are two main types of pronation: eastern and western. Eastern pronation is when the palm of the hand faces inward (toward the body) at the point of contact with the ball, while western pronation is when the palm faces outward (away from the body). Western pronation provides more power and topspin than eastern pronation, but it can be harder to control.
Overpronation
Overpronation is a term used to describe excessive inward rolling of the foot after it has landed on the ground. If you overpronate, your foot rolls inward more than normal as you walk or run. This can lead to a number of problems, including foot pain, plantar fasciitis, heel pain, Achilles tendonitis and shin splints. Overpronation is relatively common in people who have flat feet or low arches. It can also affect people with high arches if they wear shoes that are too flexible.
How to Pronate Properly
Pronation is a term used to describe the way your foot hits the ground when you walk or run. The pronation of your foot can be classified as neutral, supinated, or pronated. A neutral pronation means that your foot rolls inward and outward at an equal rate when you hit the ground. A supinated pronation (also called an underpronation) means that your foot rolls outward when it hits the ground. And a pronated pronation (or an overpronation) means that your foot rolls inward when it hits the ground.
Pronation is important because it helps to absorb shock and provides stability when you walk or run. If you have a neutral pronation, your feet are able to absorb shock evenly and maintain stability. However, if you have a supinated or pronated pronation, your feet are not able to absorb shock evenly or maintain stability as well, which can lead to injuries.
There are several ways to determine whether you have a neutral, supinated, or pronated pronation. One way is to look at the wear pattern on your shoes. If you have a neutral pronation, the wear pattern on your shoes will be evenly distributed across the entiresole of the shoe. If you have a supinated pronation, the wear pattern on your shoes will be more pronounced on the outside edge of the sole. And if you have a pronatedpronation,the wear pattern on your shoes will be more pronounced on the inside edge ofthe sole.
Another way to determine whether you have a neutral, supinated, or pronatedpronation is to have someone else look at how your feet hit the ground whenyou walk or run. If you have a neutral pronation, your feet will hit theground relatively evenly from heel to toe. If you have a supinatedpronation,your feet will hit the ground more on your toes than onyour heels. And ifyou have apronatedp ronat ion , y our fee t wi l l hi t th e g roun d mo re o n yo ur h eel s th ano n yo ur toes .
Ifyou think you mayhave asupi n atedor pro nat ed p ro nat ion , there aresevera l thin gs yo u ca n doto tr yto c orrectit . One thing yo u can dois wo rk o ut w ith b ands oro ther re sis tan ce de vices . Th e se de vices ca n helpstre ng th en th e mu scl es in yo ur leg s an d fee t whi ch wil l helpto reduceor even correctsupi nation orde formityNow!
The Benefits of Pronation
Pronation is the natural movement of the foot that allows it to absorb shock and adapt to different surfaces. When pronating, the foot rolls inward and the arch flattens. This action distributes the weight of the body evenly across the foot, providing stability and preventing injuries.
Pronation is an important part of the tennis serve, as it helps to generate power and spin. When serving, players should pronate their feet to ensure that they are able to transfer all of their body weight into the shot. Pronation also allows players to generate more topspin on their shots, which makes the ball bounce higher and travel faster.
Players who do not pronate their feet during their tennis serve often find that their shots lack power and spin. This can lead to injuries, as the player is not able to distribute their body weight evenly across their foot. Pronation is therefore an important part of the serve, and players should make sure that they are doing it correctly in order to avoid injuries and improve their game.
The Drawbacks of Pronation
Pronation can have some drawbacks in tennis. For one, players who pronate excessively can put extra stress on their ankles and knees, which can lead to joint problems down the road. Additionally, players who pronate excessively may have difficulty controlling their shots and keeping the ball in the court. If you find that you are struggling with either of these issues, you may want to ask a coach or a professional to take a look at your footwork and technique.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pronation in tennis is a very important aspect of the game. It can help you increase your power and performance, while also helping to prevent injuries. Make sure you take the time to learn about pronation and how it can help you improve your game.